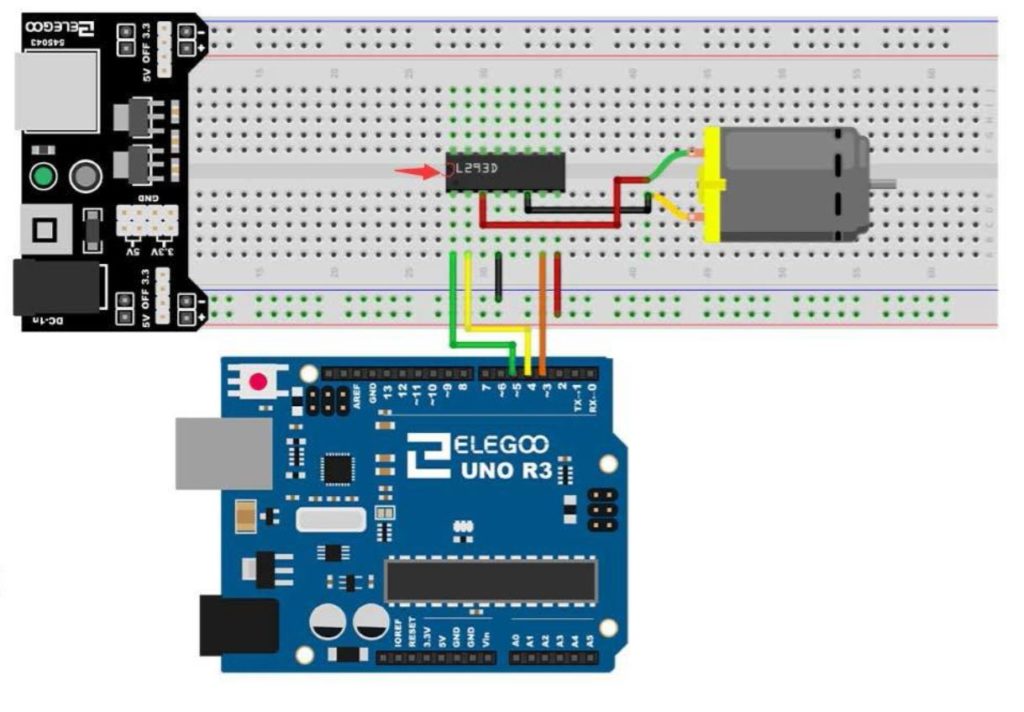
In this video lesson we show you how you can control a small DC motor using the Raspberry Pi Pico W and a TA6586 DC Motor Controller. We show you how to control both the speed and direction. The schematic for the circuit we use is here:

When using the breadvolt, or any battery power supply on a breadboard project, do not turn the power supply on while the Raspberry Pi Pico is connected to USB, as you could generate voltage conflicts. It is an either or. If the USB is connected, the power supply should be OFF. Or if you are going to connect the USB, first turn off the power supply.
In the lesson, we developed the following code for your convenience:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 | from machine import Pin,PWM import time icPin1=Pin(14,Pin.OUT) icPin2=Pin(15,Pin.OUT) fPWM=PWM(icPin1) rPWM=PWM(icPin2) fPWM.freq(1000) rPWM.freq(1000) try: while True: for speed in range(20,101,10): rPWM.duty_u16(0) fPWM.duty_u16(int(speed/100*65535)) time.sleep(.25) for speed in range(100,-1,-10): rPWM.duty_u16(0) fPWM.duty_u16(int(speed/100*65535)) print(int(speed/100*65535)) time.sleep(.25) time.sleep(2) for speed in range(20,101,10): fPWM.duty_u16(0) rPWM.duty_u16(int(speed/100*65535)) time.sleep(.25) for speed in range(100,-1,-10): fPWM.duty_u16(0) rPWM.duty_u16(int(speed/100*65535)) print(int(speed/100*65535)) time.sleep(.25) time.sleep(2) except KeyboardInterrupt: print("Program Stopped by User") rPWM.duty_u16(0) fPWM.duty_u16(0) time.sleep(.15) rPWM.deinit() fPWM.deinit() icPin1.off() icPin2.off() |